Tracking user behaviour with Aptabase
Aptabase (opens in a new tab) is an open source alternative for Google Analytics. Analytics, or tracking user behaviour, is an important aspect of understanding where most of your users interact with your app. You may want to understand:
- which screens do most of my users navigate to?
- which buttons are interacted with the most?
- which features should be developed next? For example, introducing placeholder features to assess user interaction levels
In app/(home)/aptabase.tsx, you will find two examples of tracking events to Aptabase:
- when the screen renders (to track how often a particular screen is viewed)
- when a button is pressed (to track how often a user interacts with a button)
These are just two of many examples of what you can track in your app.
Getting started
Create an account (opens in a new tab) with Aptabase to get started. Next, register a new app and give it a name.
You will then be prompted to install the Aptabase SDK. Select React Native (you don't need to follow the instructions as this boilerplate includes the library).
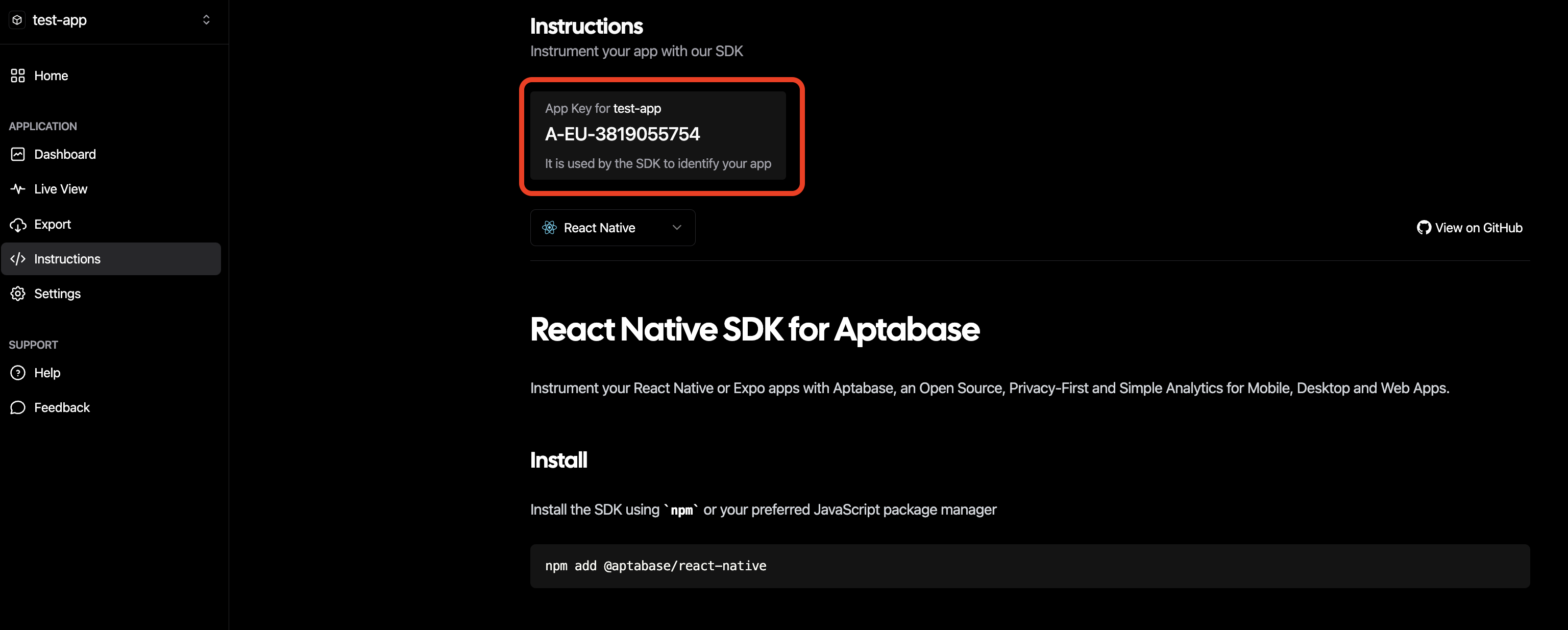
Take a note of your API key that's created (as shown above) - in your .env file, replace the default value for
EXPO_PUBLIC_APTABASE_API_KEY with the key that's been created in the Aptabase dashboard.
Tracking events
As mentioned in the usage guide, you can track events using the trackEvent method (this example is found in app/(home)/aptabase.tsx):
const { trackEvent } = useAptabase();
trackEvent("event-name", { foo: bar });After a few seconds, events will start to appear on the Aptabase dashboard. You can also see more data about the events, such as the location of the event that was emitted (only narrowed down to country), the operating system of the device and the app version.
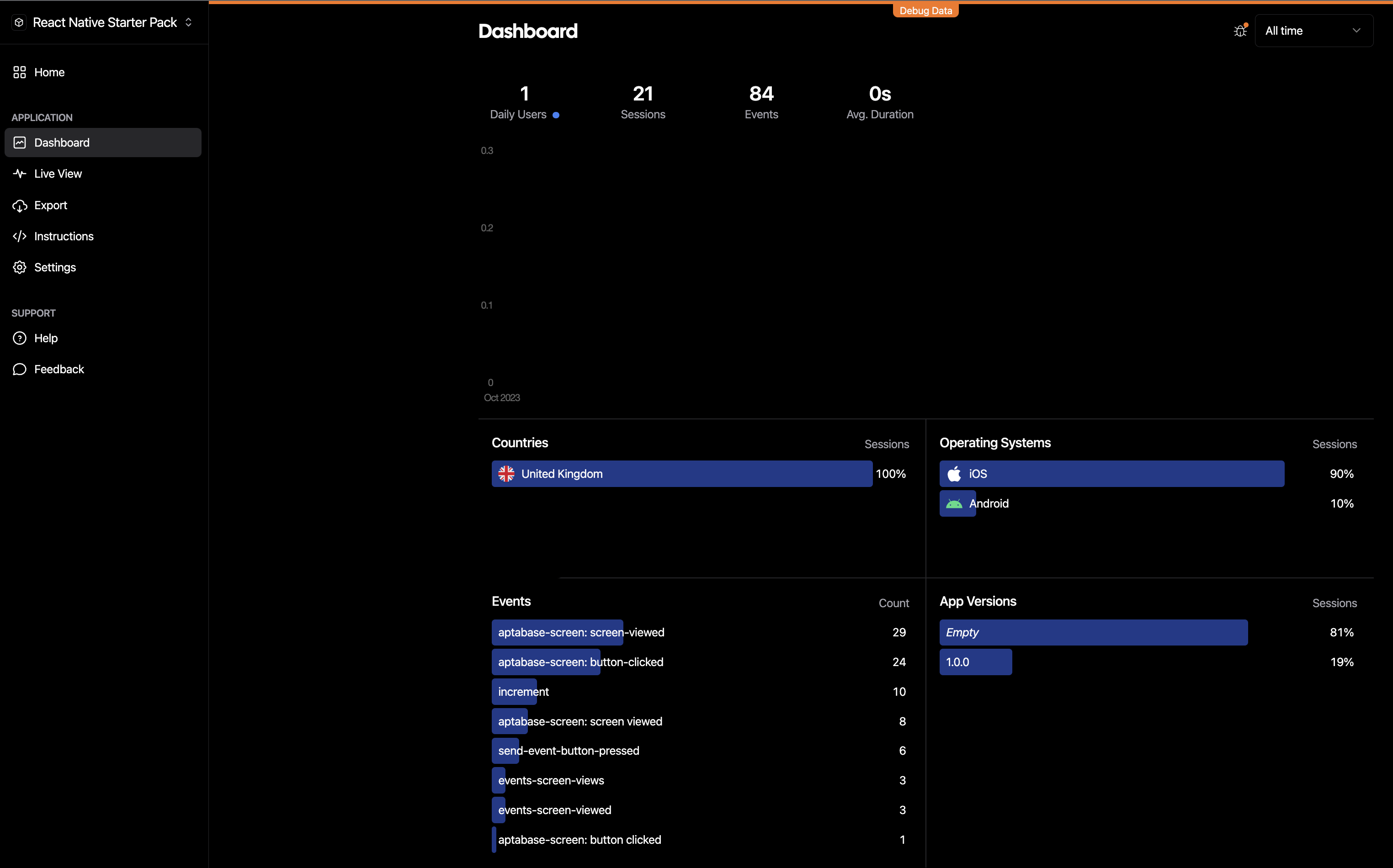
Permissions Guidance
In compliance with Apple's Guidelines, all applications must request user consent prior to tracking their activities across other companies' websites or apps for advertising purposes or before sharing their data with data brokers. Users have the flexibility to grant or withhold this permission and may alter their decision at any time. Additionally, users retain the option to prohibit all apps from making such requests. You can check the guidelines here (opens in a new tab) and more information user privacy and data use here (opens in a new tab).
Best Practices for User Tracking
To effectively track user engagement, it is important to define the specific metrics you aim to monitor and identify clear indicators of success and failure. For example, a higher frequency of visits to a particular screen may indicate that users find value in the content or functionality it provides. Leveraging analytics can also forecast the potential popularity of new features. Introducing a prototype feature and gauging user interest based on number of visits to a particular screen or interactions with components on the screen can provide invaluable insights.
Limitations of Aptabase
It is important to note that Aptabase does not track unique event occurrences. Repeated visits to a screen by a single user are each recorded as separate events. If you're looking to capture unique interactions, such as first-time screen views or distinct button clicks, you'll need to enhance Aptabase's existing functionality. This could involve implementing a local key on the user's device to determine event emission based on new or repeated activity.
For more information, please refer to the Frequently Asked Questions section (opens in a new tab) of the Aptabase docs.
Demo
Once you've created the correct table and storage bucket in Supabase, you should be able to persist and manipulate data from the app as shown in the demo: